Blockchain Byte - Week 2 : It's all about the money

We all use money. Money can be in physical form represented by notes or coins or in digital format.
Money is anything that serves as a medium of exchange
A medium of exchange is anything that is widely accepted as a means of payment. The usage of money is ultimately defined by people and what they do with it. When people use something as a medium of exchange, it becomes money.
Why do we need money? Or what is the function of money in society?
Money serves the following three basic functions:
- A medium of exchange
- A unit of account
- A store of value
Let us explore each of the above:
A medium of exchange
We all either buy or sell goods or services. Such transactions or exchanges should be friction less meaning there should be something common as a medium of exchange. E.g., it is not practical to exchange fish for a pizza (though it is not impossible!). Both the buyer & seller use money to exchange goods or services. Here, fiat currency or money is a common denominator in any exchange
A unit of account
Continuing from the above, we measure what we buy or sell in terms of some value. This value is represented by money which serves as a unit of account. Thus there is a consistent means of measuring the value of things. We use money in this fashion because it is also a medium of exchange. Nobody says "I paid five pizzas for this phone". They say "I paid $200 for this phone"
A store of value
The third function of money is to serve as a store of value., i.e., an item that holds value over time. Normally, it maintains it's value over time, instead of depreciating (let us ignore inflation for the time being!). Another example of items with good store of value is gold and other precious metals.
Let us deep dive into money as we know it.

Fiat Money
Fiat money is money that some authority, generally a government, has ordered to be accepted as a medium of exchange. The currency that we use - paper money & coins is fiat money; it has no value other than its use as money.
Fiat money is issued by Central Banks. So a note of fiat currency is a liability in Central Bank books. So the only way a retail customer has access to Central Bank ledger is through fiat money. This is also called Central Bank money.
Now, what about money in deposits / checking accounts with banks? This is called commercial money.
Commercial Money
Commercial Money is a digital version of fiat currencies which are represented by balances in ledgers of banks where the funds are held and where movement of funds is shown as reduction in balance of the sender’s account and increase in balance of the recipient’s account.
In accounting parlance, the sender’s account is debited and recipient’s account is credited. So the movement of money is recorded between ledgers of both banks - sender and receiver bank. The balance in the receiver's account goes up and the balance in the sender's account comes down.
A very simple representation of such a transfer is shown below
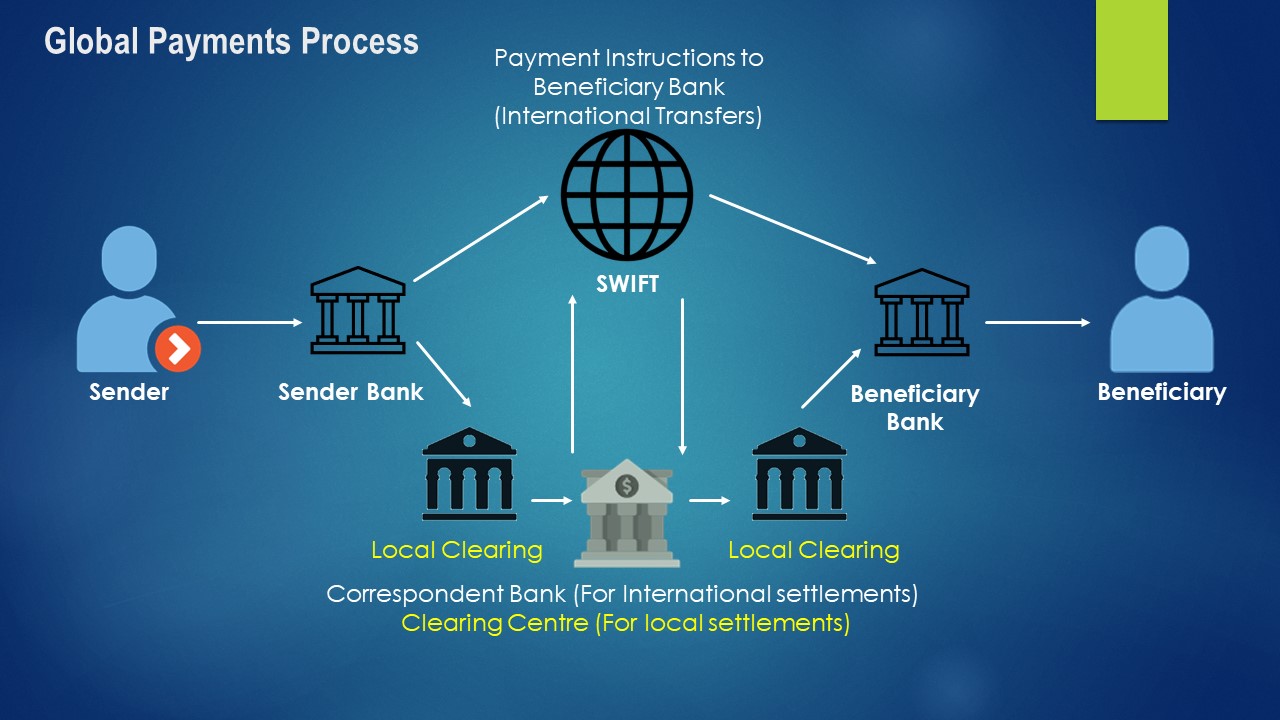
Transactions can be local or international.
International Transactions
International transactions happen through a network known as SWIFT. SWIFT means Society for Worldwide Inter-bank Financial Telecommunication. It provides a network that enables financial institutions worldwide to send & receive information about financial transactions in a secure, standardized & reliable environment. (More on swift here)
Local Transactions
Local transactions are normally routed through a clearing house. Local clearing applies to funds transfers (through cheques or electronic payment requests) within a jurisdiction. (More on clearing here)
When you move money across banks in the same jurisdiction or different jurisdictions, these banks act as trusted intermediaries to ensure
a) The sender actually has the funds to initiate the transfer
b) The sender is actually who he claims he / she is
c) The funds actually move to the recipient's account
Even when we do online payments through other intermediaries like PayPal, they sit between the buyer & seller and act as trusted middlemen to ensure the above conditions are met.
The above intermediaries / middlemen add to the cost of transferring funds. They take their fees / commission to provide the above mentioned services.
But why am I explaining about money, its functions & payments process in the context of blockchain?
Well, the first & the most popular use case of blockchain is Bitcoin, the first true digital currency or cryptocurrency — a new paradigm as it is the first digital currency without any Central Bank backing, with its own store of value and not a representation of any underlying fiat currency.
