Blockchain Byte - Week 5 : What is Blockchain?

Table of Contents
Recap
What is a Blockchain?
Ledger
Comparison with existing infrastructure
" I've been working on a new electronic cash system that's fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party." - Satoshi Nakamoto
Recap
To recap, last week we touched upon:
- Transfer of Value
- The concept of trust on transfer of value - an authority or intermediary will verify the identity of the parties & ownership of assets or money being transferred
- The version of truth maintained by intermediaries / central authorities through registers, certificates etc.
- The problem of double spending
- Meaning of peer-to-peer
- Failure of earlier attempts to create digital currencies and reasons for the same most notably centralization and the problem of double spending
Now, let us answer the question that was asked from week 1
What is a Blockchain?
To put it very simply - We can define blockchain as
A system that allows a network of connected computers to maintain a single, updated & secured ledger
So, the key terms of the above definition are
- A System
- A network of connected computers
- A single, updated and secured ledger

Ledger
What is a ledger? - A ledger is a principal book that records all the accounts of your business like expenses incurred, income earned, assets owned, liabilities owed etc. For more details on ledgers, please refer here
The below shows a simple transaction where a sender sends $50 to a beneficiary and how it impacts the ledger of each bank
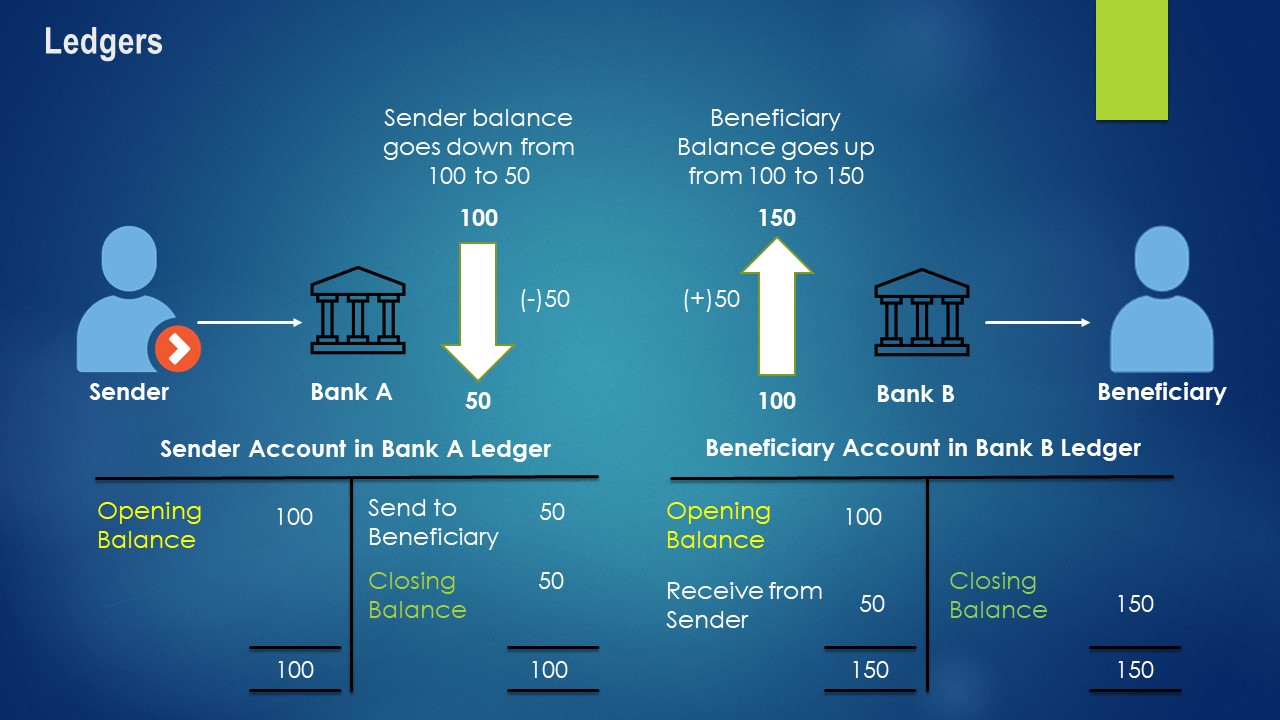
Now, how can a group of interconnected computers maintain the same ledger, update it at the same time and then keep it secure?
Comparison with existing infrastructure
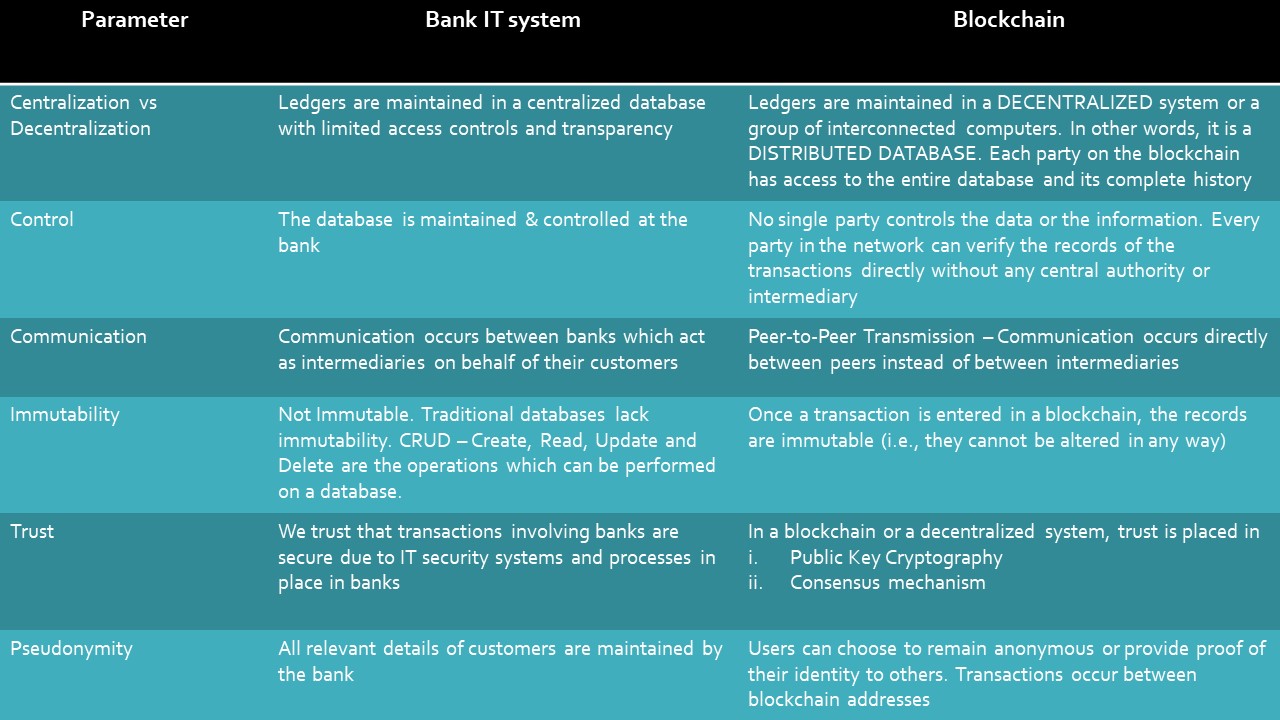
Let us start with certain key parameters & compare them with an existing infrastructure so that we can visualize the difference. Note that the Blockchain used for comparison is a Public Blockchain.
- Decentralized network
- Control
- Mode of Communication between parties
- Immutability of transactions
- Trust
- Privacy, anonymity / pseudonymity
With the above basic understanding in place, let us dive in by expanding on each of the above points & introduce other concepts as we move forward.