Strategy Byte - Week 19 : Forex Drivers & Impact

Table of Contents
- Recap
- Impact on Performance
- Linkage to Strategy
- Foreign Exchange Drivers
Recap
During Week 18, we explored "Exchange" which is "The act of giving something to someone & them giving you something else."
Using apples & oranges being exchanged in a market as examples, we defined a market & jumped to Demand & Supply as a driver for change in value of a product.
We then defined "Forex Market" as a global, decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for trading of currencies.
This week, let us explore why foreign exchange is an important external environment variable in strategy & what drives it.
Impact on Performance
Why is foreign exchange rate an important external environment variable for strategy purpose? If a company is a global company or a multinational company, it will have operations in multiple countries or jurisdictions. Even local companies may have transactions to import raw materials or export their finished goods. That means dealing & transacting in different currencies which can impact
- A single transaction or multiple transactions over a period of time or
- Transactions embedded into the balance sheet which can impact a company's performance over a financial period or multiple financial periods.
How do we analyze the performance of a company? Through it's financial statements & more specifically the "Income Statement". What is an income statement?
The Income Statement is one of a company's core financial statements that shows their profit & loss over a period of time. The profit or loss is determined by taking all revenues & subtracting all expenses from both operating & non-operating activities". (Source : here).
Visualizing the above through a very basic income statement:
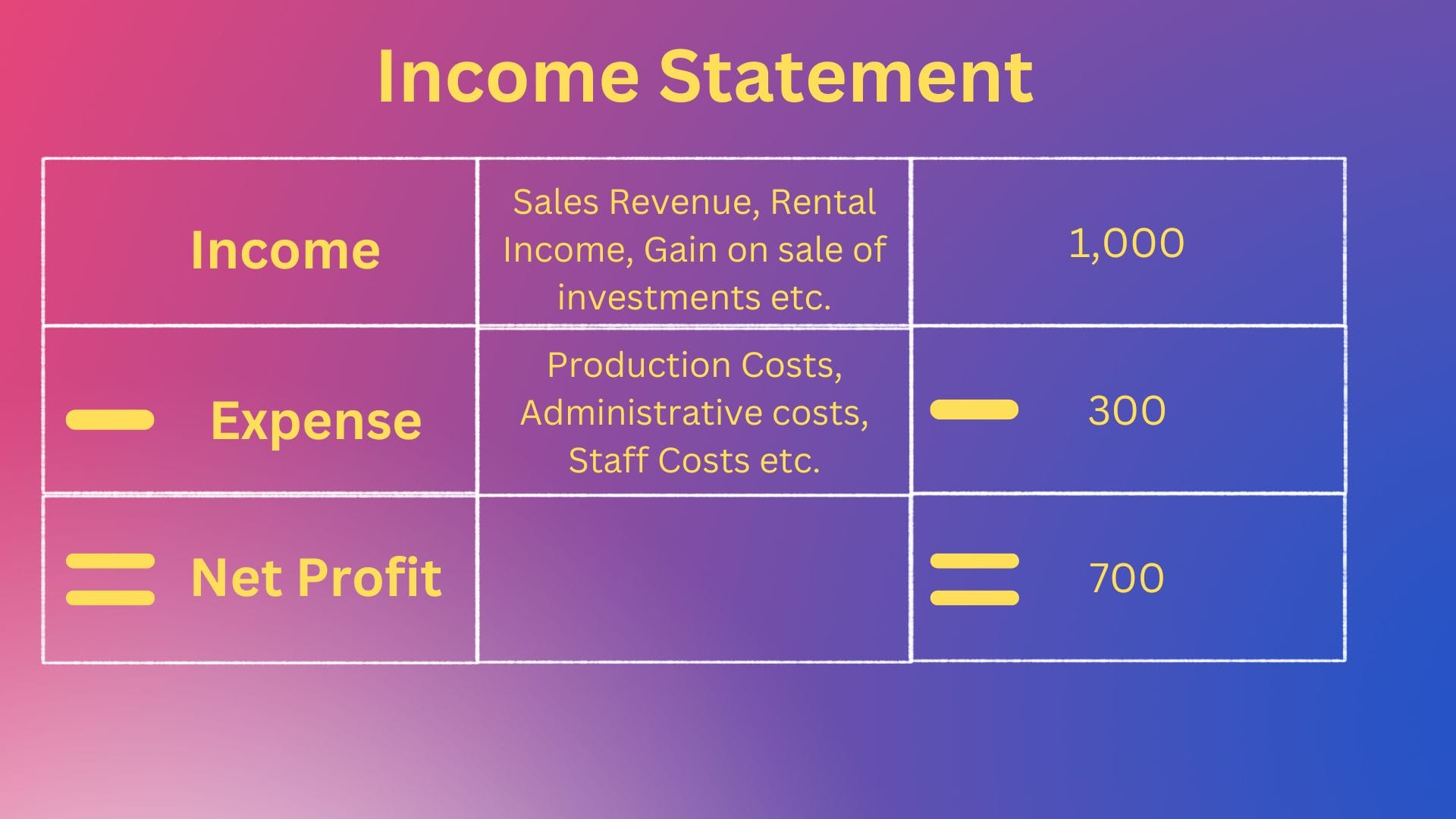
What has foreign exchange got to do with a company performance? Let us explore:
A Single Transaction or Multiple Transactions
In this globalized economy, a company can purchase raw materials from anywhere in the world. Assume that a local company with local currency LCY purchases 1000 tons of raw material from US @ 100 USD per ton. So the local company has to pay in total:
Raw material purchase cost = 1000 tons @ 100 USD/ton = USD 100,000.
Assume payment has to be done twice in three months,
- First payment on order placing - USD 50,000 &
- Second payment on delivery - USD 50,000
Assume exchange rate is 1 USD = 2 LCY
So total payment in local currency = 100,000 * 2 = LCY 200,000.
Let us visualize it below:
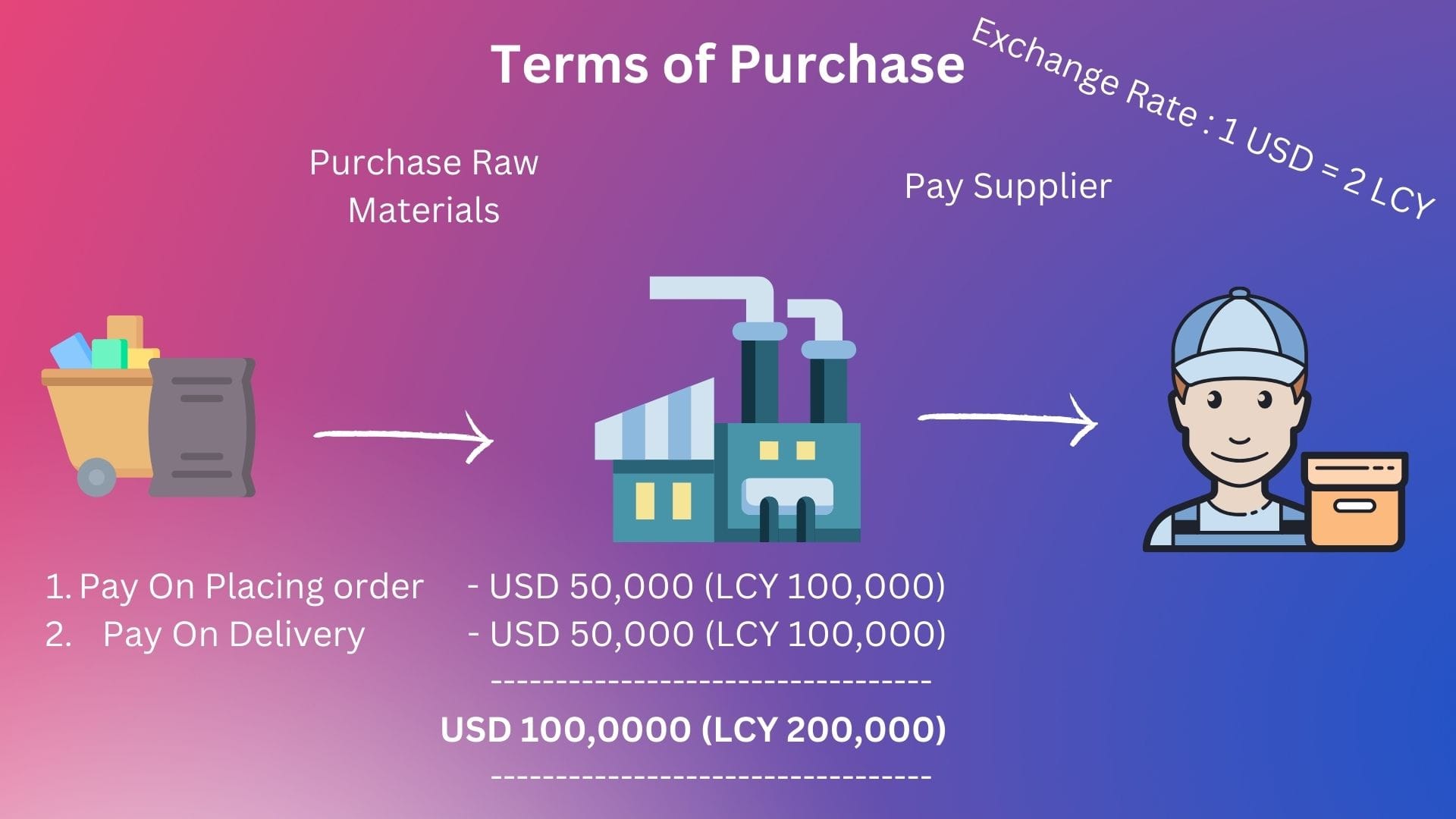
If there is no change in exchange rate during this time, the company would exchange total of LCY 200k to pay USD 100k to the foreign supplier of raw materials.
In the Income statement, the transaction would show as below:
Raw Material Purchase (Under Expenses) = LCY 200,000
But this is not how the real world works, foreign exchange rates fluctuate every day. Let us assume that the rate changes just before payment on delivery as
1 USD = 2.5 LCY. Then, the total payment in LCY changes as below:
Raw Material Purchase (Under Expenses) = LCY 225,000
Visualizing the above:
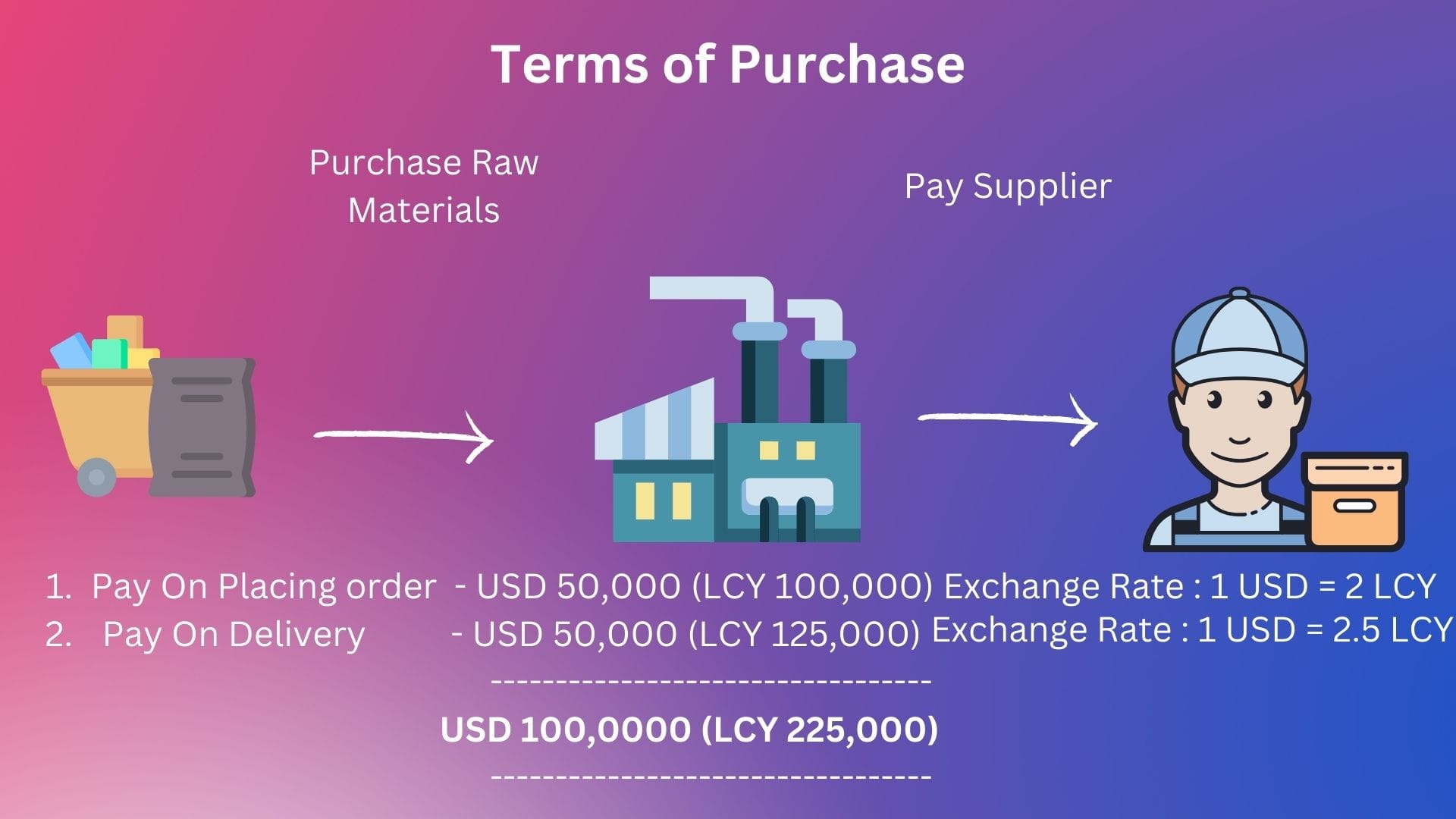
So, in the second scenario, the expenses increased by LCY 25k thus reducing the profit by the same amount. In other words, the company pays more in local currency.
Below visualization gives a comparative picture of both scenarios (assuming for simplicity sake this is the only expense):
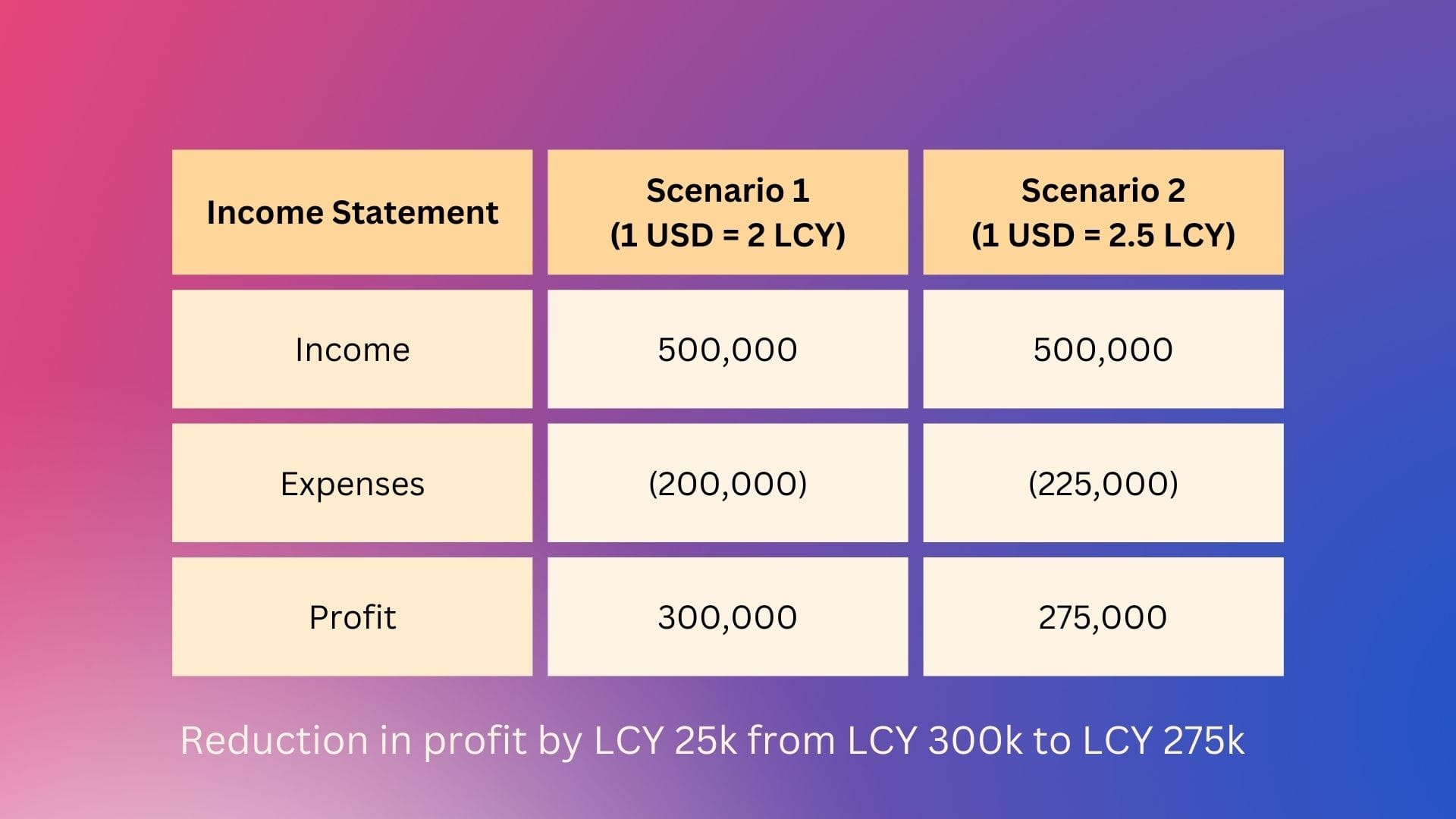
To be clear, there are tools like forex hedges & swaps which are used to manage such fluctuations in exchange rates & hedge (protect) against such currency fluctuations. But the scope of our discussion is only to understand the impact of currency fluctuations on a company's performance.
Now, on the flip side, if the rate moves in the opposite direction, that can result in unexpected gains or profits in the income statement. How?
Let us assume (Scenario 3) the rate of LCY against USD becomes 1 USD = 1.5 LCY at the time of second payment on delivery. Then the above comparison looks like:
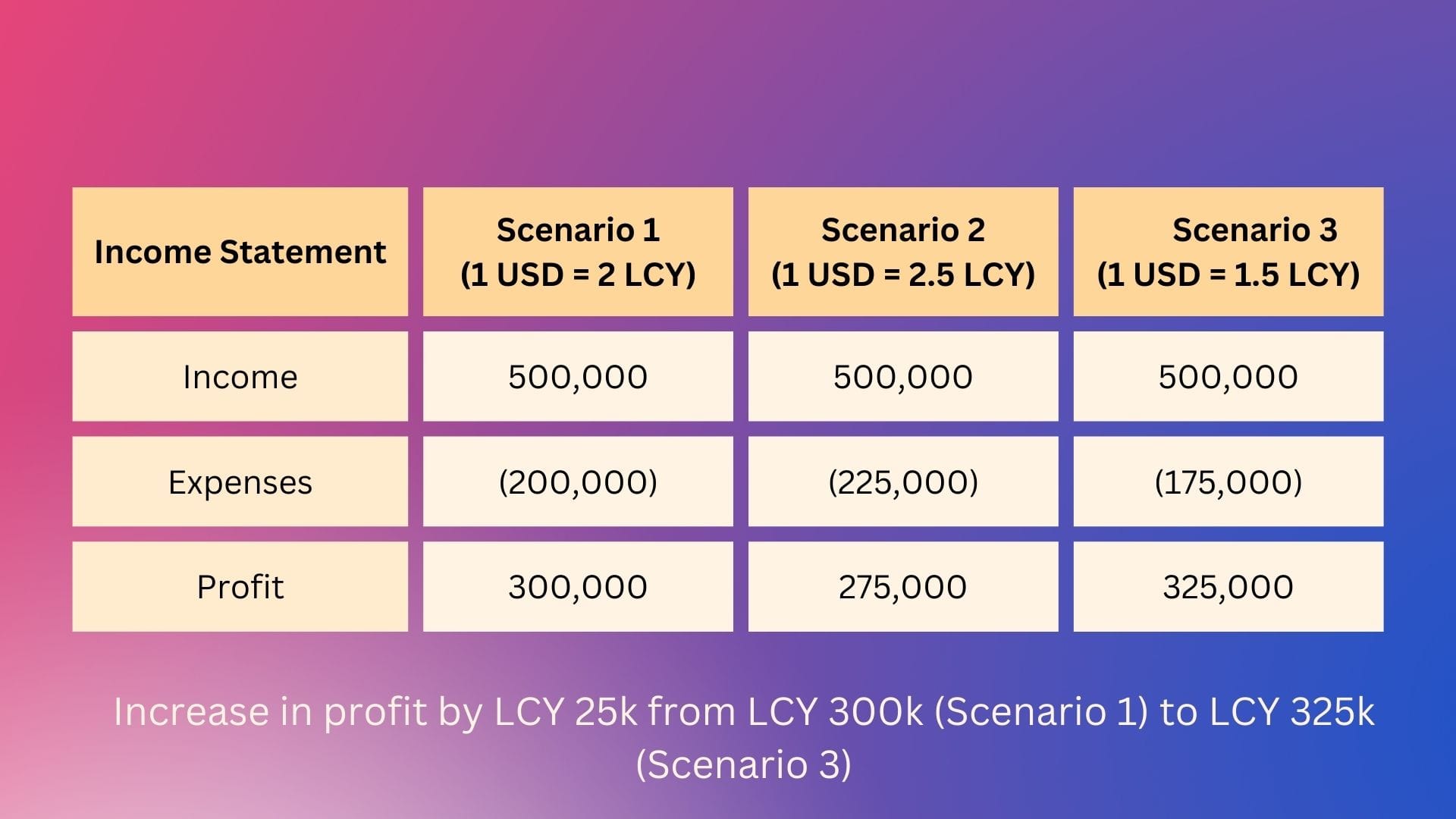
But the problem is that this fluctuation is unpredictable & hence the impact can also be unpredictable - the fluctuations can result in either gain or loss.
Transactions Embedded into the Balance Sheet
If a company invests in another country by having a subsidiary or investment in an overseas company, it is subjecting itself to currency risk in the balance sheet because it pays for the investment in foreign currency & has to disclose the amount in local currency which keeps changing each balance sheet date. Why?
Once the parent company brings the overseas investment into it's own books, it has to convert the amounts from that foreign currency to it's own local currency each balance sheet date which can result in changes in it's financial statements due to translation of numbers from foreign currency to local currency.
A simple example is if an Indian company buys a property in US in USD, it has to part with INR to pay the seller in USD. This amount is disclosed in it's balance sheet in INR & at each balance sheet date, this number will keep changing depending on exchange rate fluctuation.
Linkage to Strategy
If a company has a strategy which involves outsourcing operations or investing overseas or opening new production facilities overseas, this is a very important external environment variable to consider.
We discussed above how exchange rate fluctuations impact a company's performance & balance sheet. In this interconnected world, it is not only multinational companies which are impacted by foreign exchange fluctuations. Even local companies whose strategy involves either importing from or exporting to other countries are impacted by such fluctuations.
Even if a company has excellent products with good demand, where these products are manufactured, exported, imported etc makes a lot of difference to the ultimate financial impact - the bottom-line or net profit. The result of a good strategy ultimately shows up in net profits due to better performance or better market share than peers or competitors.
As I mentioned above, there are tools to manage foreign exchange fluctuations but those are more of managing it at operational level. But if the strategic decision to outsource or manufacture overseas does not consider this factor, it can impact their future performance.
It is a very important variable to keep an eye on but to be seen in conjunction with other external environment variables (Which we will get into in the coming weeks). Just as we saw last week, demand for oranges increased the price of oranges in comparison to apples, let us explore what drives foreign exchange rates.
Foreign Exchange Drivers
The macro economic variables of a country are all correlated & any fluctuation or change in one variable impacts the other either positively or negatively. However, just as a company's share price is driven by it's performance as well as expectations of it's future performance, a country's economic outlook is a key driver of that country's currency value & exchange rate. The other major (the Forex market is complicated & hence not all factors influence currency values equally) drivers are :
- Interest Rates
- Relative Inflation Rates
- Current Account Balance in BoP (Balance of Payments)
- Economic Growth Rates
- Competitiveness
Let us take a high level look at each factor & how it impacts foreign exchange rates.