Strategy Byte Week 51 - Automotive Industry Analysis - Part II

Table of Contents
- Recap
- Value Chain Analysis - Level 2
- Key Players
Recap
During Week 49 of Strategy Bytes, we started our journey into industry analysis with the Automobile industry. Why did we start with automobile industry? Because it holds a special place in our hearts - The first upgrade in our life comes with our first car. Who doesn't remember their first car?
Discussion Template
For a structured discussion, we started with the below template for our analysis (this will be used in all future discussions & analysis, so worth repeating) :
- What is the automotive industry? How is it segmented?
- How is the value chain structured in the automotive industry?
- Who are the players in the value chain of the automotive industry?
- How does each player contribute to the value chain?
- How is each player positioned vis-a-vis their competitors?
- What are the important customer segments?
- What are the regulations governing the automotive industry?
- What is the unit economics of the industry?
- What are the new developments or disruptive forces in the automotive industry?
Industry Segmentation
We first discussed segmentation by vehicle type as visualized below :
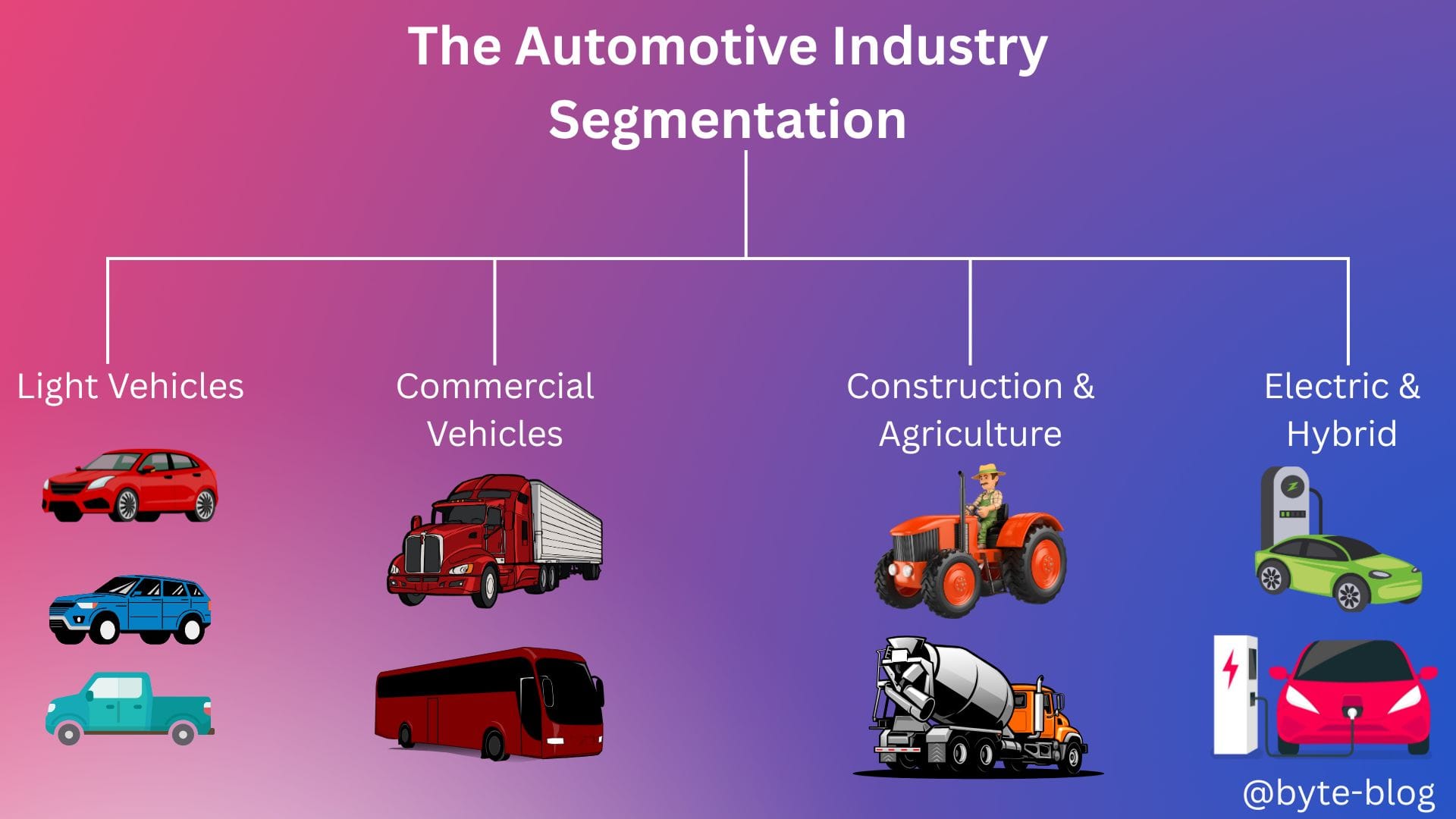
We then dug deep to cover Value Chain Analysis.
Value Chain Analysis
For easier chain of thought, we analyzed this at two levels :
Value Chain Analysis - Level 1 : Which covers all activities starting from conception of the product (automobile) till the final delivery to the customer with each activity adding value at different stages.
Research categorizes the value chain into three primary segments :
- Upstream Segment - includes
- Raw Material Suppliers (Tier-3)
- Component Manufacturers (Tier-2) &
- System Suppliers (Tier-1)
- Midstream Segment - dominated by OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) who design, manufacture & assemble vehicles
- Downstream Segment - Comprises dealership networks & after-sales services
These are visualized below :
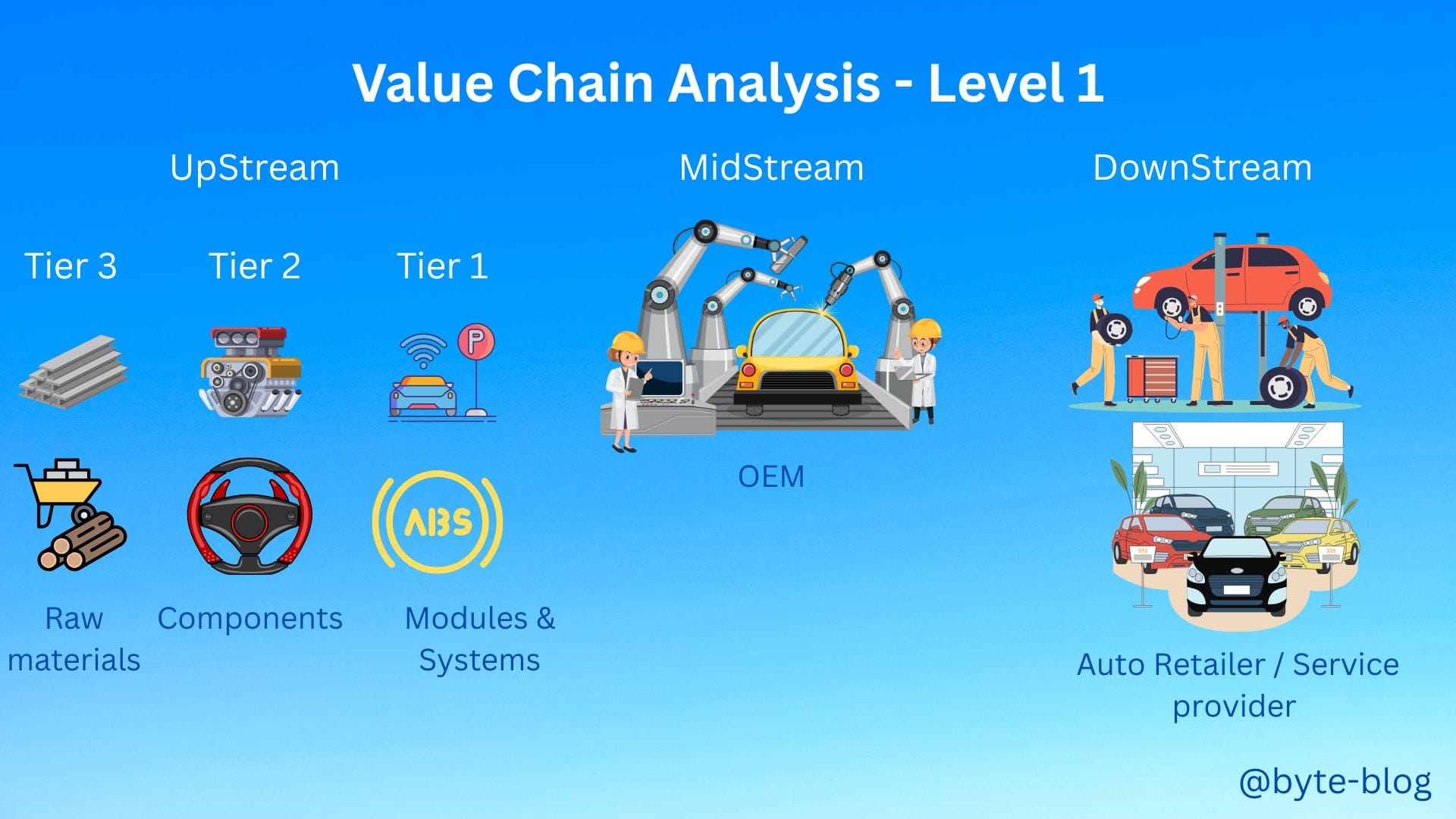
With that understanding, let us now dive deeper into Level 2.
Value Chain Analysis - Level 2
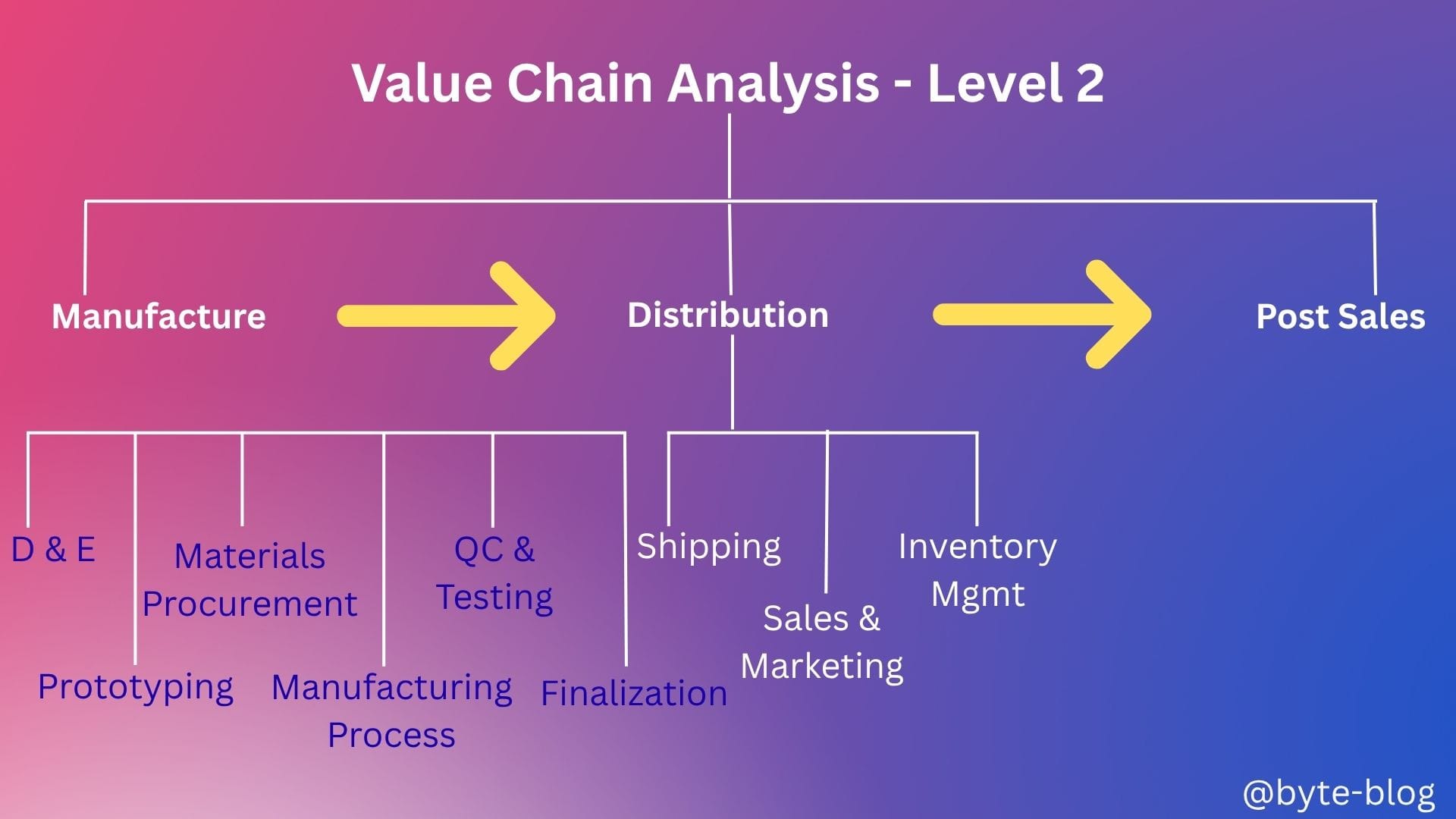
In Level-2, we will breakdown the end to end processes from concept to sale of an automobile & after sales service as :
- Manufacture
- Distribution
- Post Sales
Visualizing the above :
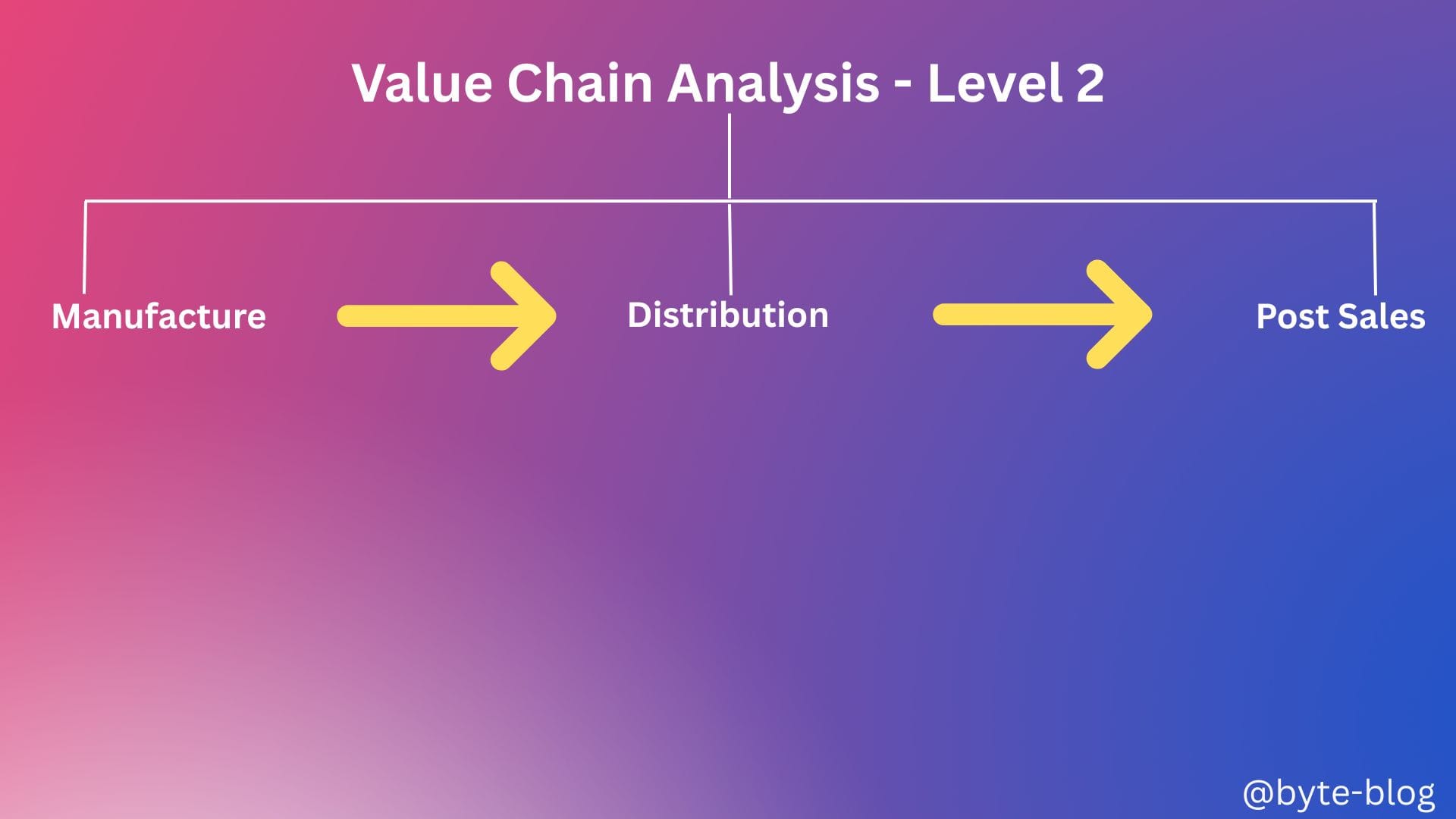
We will add to this chart as we move forward.
Manufacture
At a high level, the manufacturing process of an automobile consists of the below six steps (Source : various reports):
- Design & Engineering (D & E)
- Prototyping
- Materials Procurement
- Manufacturing Process
- Quality Control (QC) & Testing
- Finalization
Design & Engineering (D & E)

There are two steps in Design & Engineering :
- Conceptualization - This iswhere initial ideas are turned into sketches & digital models for development
- Engineering - The design is then engineered for functionality, safety & manufacturability taking into consideration materials, performance aspects etc.
Prototyping

Prototyping involves :
- Prototype Creation : This includes construction of physical models to test design ideas, aerodynamics etc
- Prototype Testing : Prototypes undergo rigorous testing for safety, durability & performance. Feedback from these tests are then fed back into the process to improve the prototype.
Materials Procurement
Materials Procurement involves :
- Sourcing : Manufacturers source raw materials (steel, aluminium, plastics, rubber etc) & components (engines, electronics, etc) from suppliers
- Quality Control : Incoming materials are inspected to ensure they meet specified quality standards
Manufacturing Process

Manufacturing Process Involves :
- Stamping : Large sheets of metal are stamped into body panels using hydraulic presses
- Welding : Panels & parts are welded together to form the vehicle's frame & body
- Painting : The body parts are painted to provide durability & aesthetic appeal
- Assembly : The various parts of a vehicle (engine, transmission, interior, wiring etc) are assembled in a specific sequence using assembly lines
Quality Control (QC) & Testing
QC & Testing involves :
- Assembly Inspection : Every car is thoroughly inspected during & after assembly to ensure it meets quality standards
- Dynamic Testing : Vehicles are subjected to performance tests on track to simulate different driving conditions
- Safety Testing : Safety features & overall vehicle performance are tested according to industry standards
Finalization
This is the final step which involves :
- Detailing & Cleaning : Finishing touches are added, such as waxing the exterior, ensuring cleanliness & checking all features are working properly.
- Documentation : Vehicles are labeled & paperwork completed for registration & warranty
Including the above into our visualization :
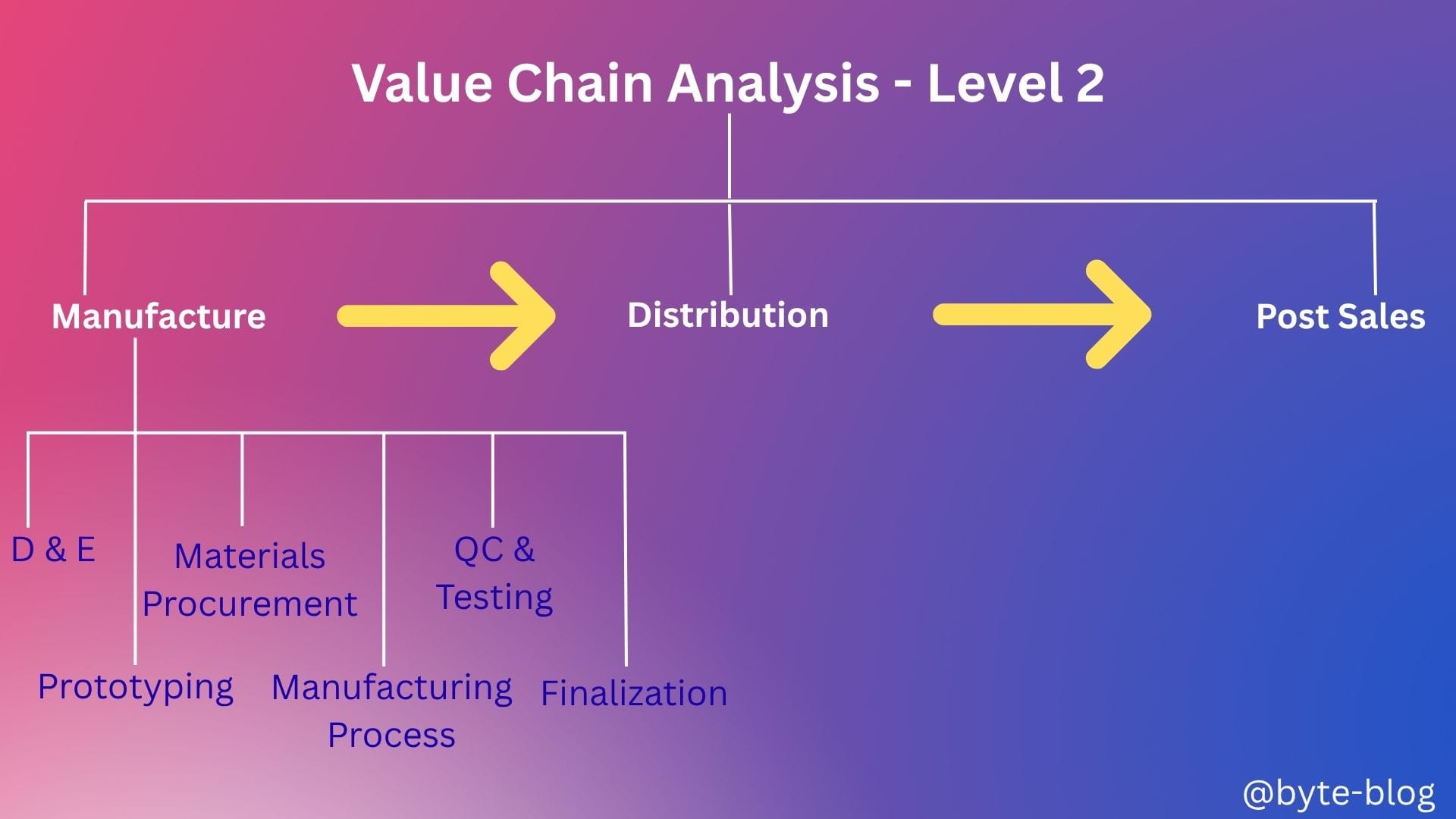
Let us now see the processes under Distribution.
Distribution


Distribution involves :
- Shipping : Finished vehicles are distributed to dealerships & markets through logistics networks
- Sales & Marketing : The vehicles are marketed & sold to customers, often involving financing & promotional offers
- Inventory & Management : Automakers & dealerships manage inventory levels to ensure availability. Advanced inventory management systems help track & optimize stock levels
Updating our visualization :
After manufacture & during distribution, the vehicles are sold to customers. Let us now look at the processes after sales to customers.
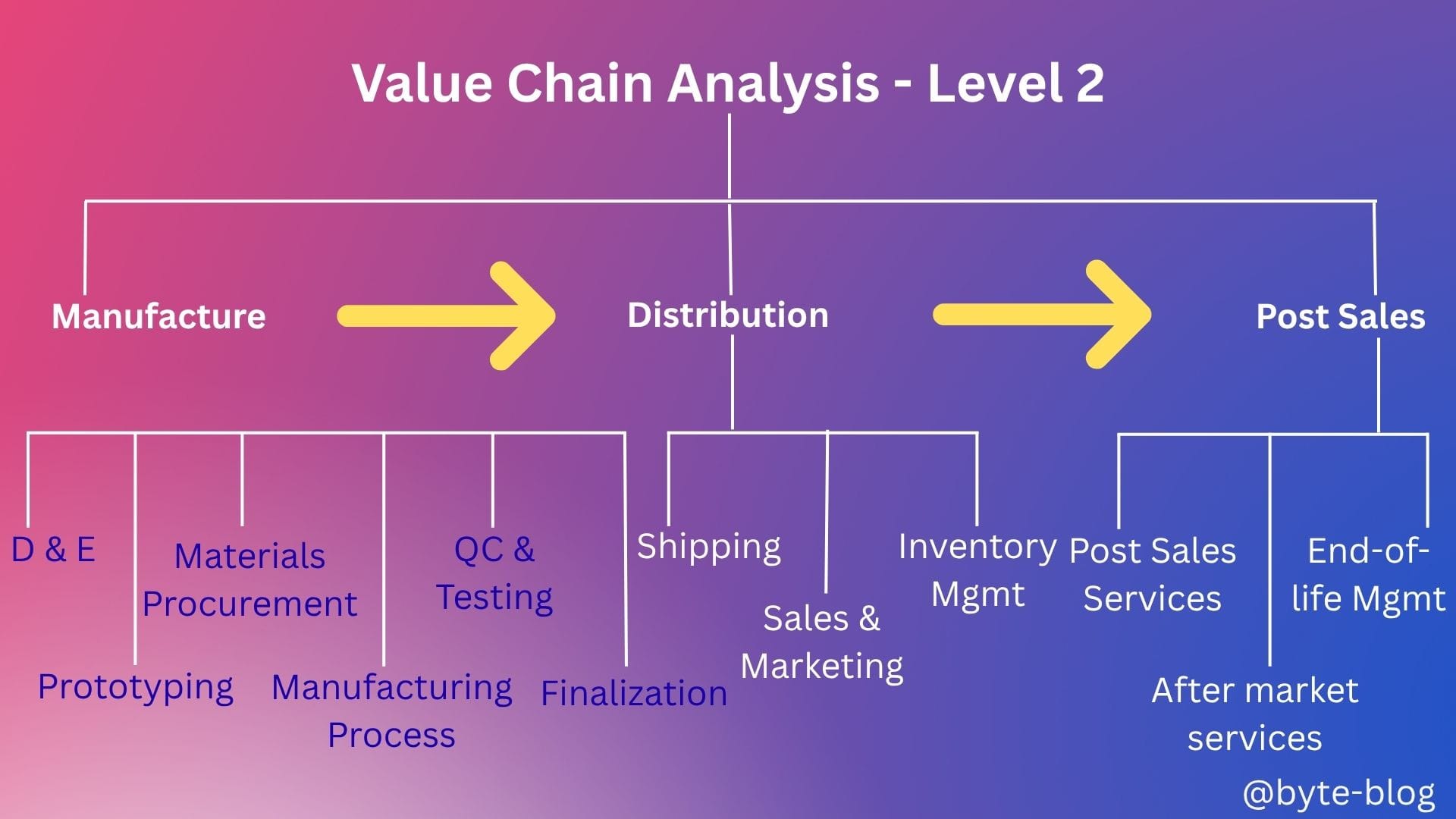
Post Sales
Post Sales involve :
- Post-Sales Services : There are two services involved here :
- Vehicle Registration - Registering vehicles with local authorities
- Warranty & Maintenance - Automakers offer warranties covering repairs & maintenance during warranty period.
- After Market Services : This involves service & repair where dealerships & independent repair shops provide services for maintenance, repairs & upgrades.
- End-of-Life Management : This involves :
- Recycling & Disposal : When vehicles reach the end of their life cycle, automakers and recycling centers work to recycle or dispose of them in an environmentally friendly manner.
- Sustainability Initiatives : Many manufacturers invest in sustainable practices to reduce their environmental footprint throughout the life cycle of their vehicles.
Updating our visualization, below is the full value chain at a high level for the automotive industry :
Key Players
Now that we understood at a high level the value chain of the automotive industry, we will now see who are the key players involved at each stage of the value chain.
Below is a breakdown of the key players are each stage of the Value Chain (Source : various reports) :
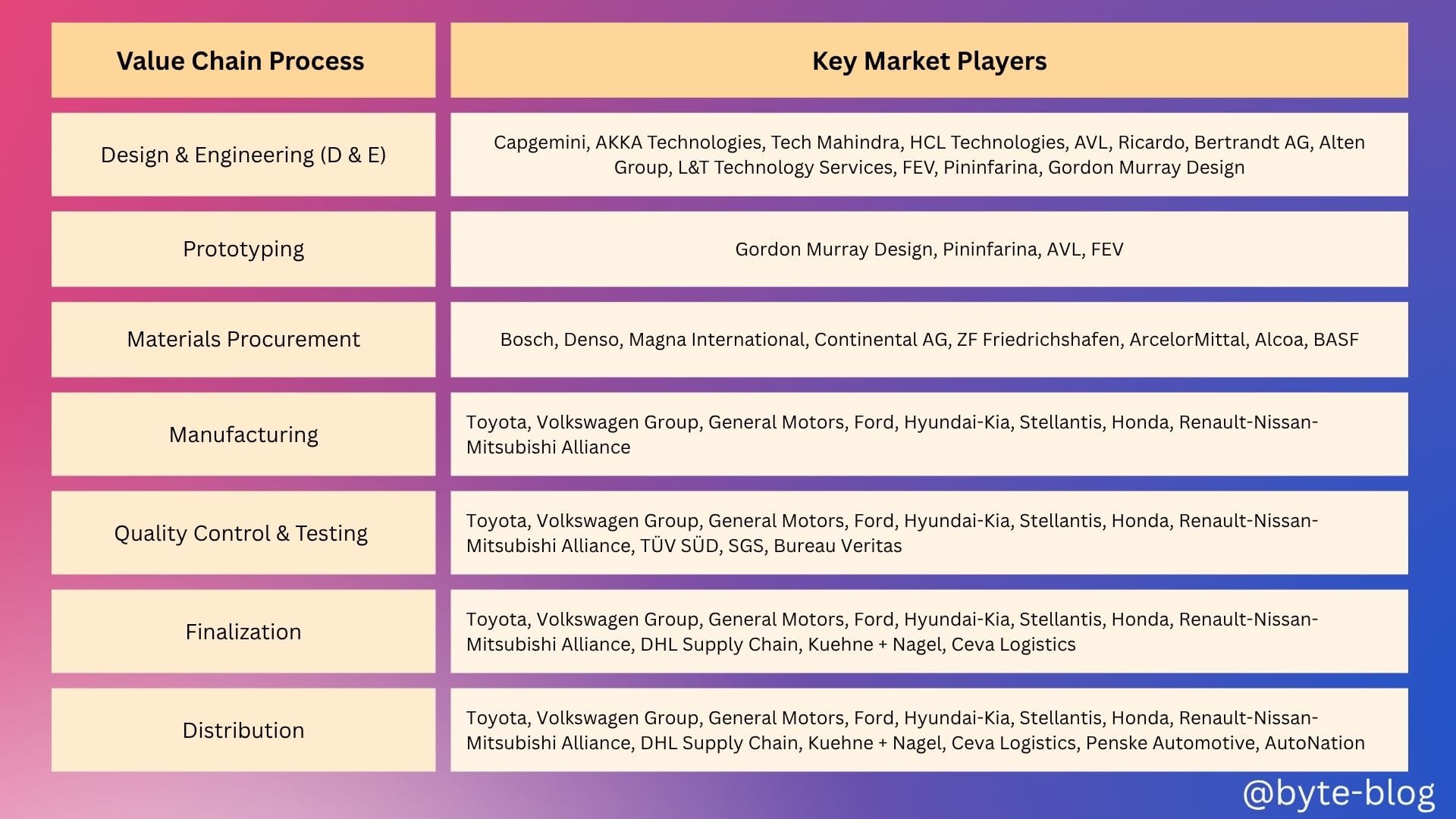
Now, after seeing the above table, do you feel something is missing? I definitely did. You would notice that Tesla is not mentioned anywhere in the value chain despite being one of the key players in the automotive industry under Electric Vehicles. So I dug in to understand why. Below are the key reasons :
- Tesla’s absence from the the above table is mainly due to its distinct operational model and focus on electric vehicles, which does not fit the traditional value chain of automobile manufacturing.
- Tesla is vertically integrated, handling everything from design to direct sales, and does it's own manufacturing & distribution (e.g., Gigafactories, direct-to-consumer sales etc).
Next week, we dive into numbers to :
- Analyze the industry as a whole
- Analyze how does each player contribute to the value chain