Strategy Byte - Week 58 The Crystal Ball - Part 1

Table of Contents
- Recap
- The Framework
- Current Industry Trends & Challenges
- Transformative Disruption
Recap
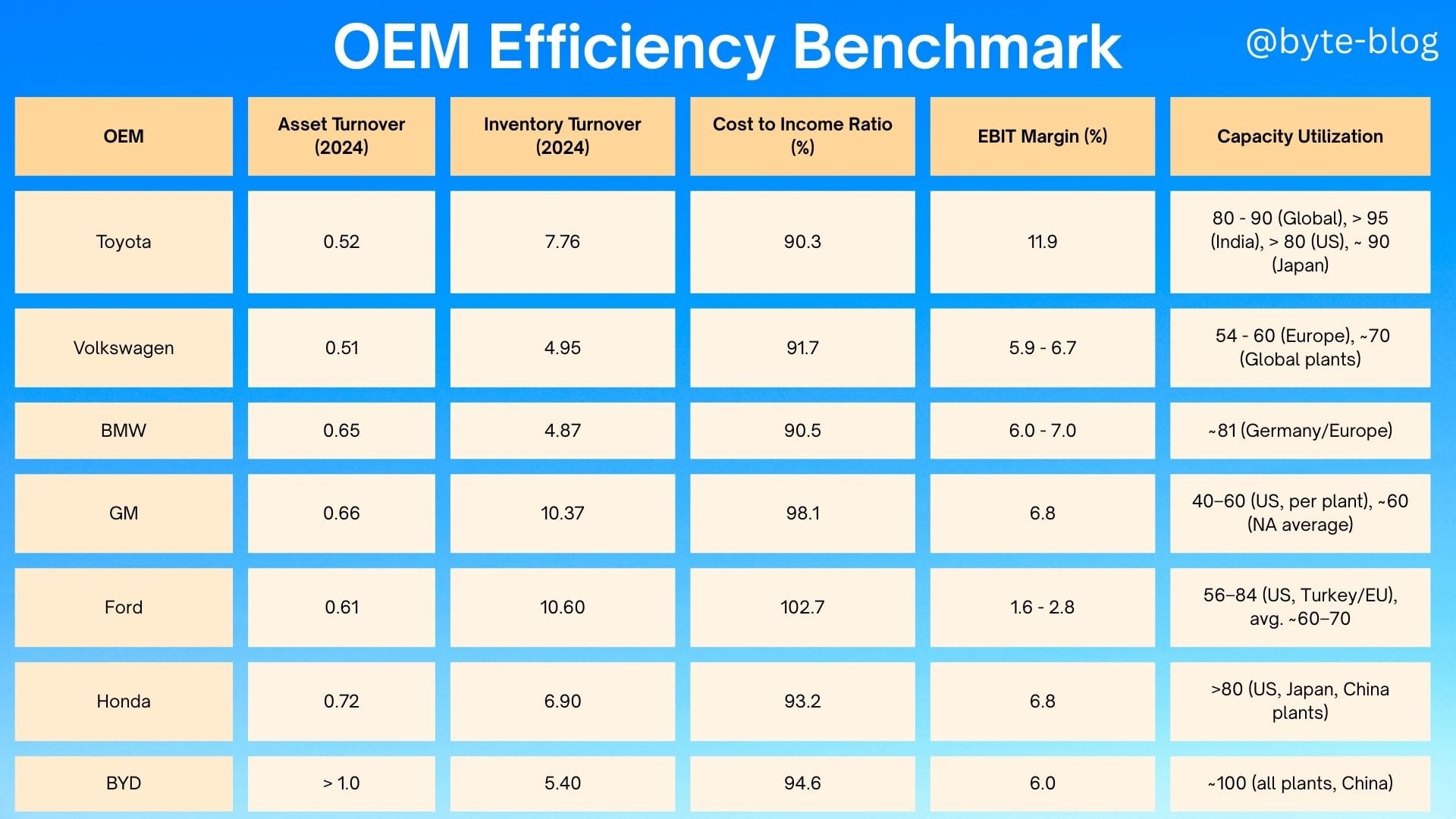
During Week 57 which was the penultimate episode of the automobile industry, we explored the below efficiency metrics of the automobile industry :
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio &
- Capacity Utilization
Asset Turnover Ratio
The Asset Turnover Ratio is an efficiency ratio which measures how efficiently a company uses it's assets to produce revenue or sales.
Thus higher revenue or sales per dollar (or any other currency) of asset invested means higher efficiency in usage of those assets.
The ratio needs to be viewed in the context of industry characteristics like whether it is capital intensive or not.
For the automotive industry, we saw that :
- The asset turnover ratio is mostly below 1 for the established players in the OEM value chain. This is mainly due to high asset base (highly capital intensive) & revenue in a highly competitive industry which keeps the ratio below 1.
- Efficient / lean automakers & aggressive entrants like BYD can exceed industry benchmarks.
Capacity Utilization
Capacity Utilization refers to the manufacturing & production capabilities that are being utilized by a nation or enterprise at any given point in time. It is the relationship between the output produced with the given resources & the potential output that can be produced if capacity was fully utilized.
One key point to note is that - higher the capacity utilization, the lower the cost per unit of output.
Why? This is because fixed costs which go towards maintaining the huge capital investments & assets (Plant & Machinery, factories, manufacturing facilities etc) is absorbed by a larger volume of output which in turn reduces the cost per output unit.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
The inventory turnover ratio is a financial ratio showing how many times a company turns over it's inventory in a given period, typically a fiscal year.
It shows how operationally efficient a company is in manufacturing what is expected to be sold in line with demand. Higher the ratio, the better it is as it signifies that inventory is being sold faster which results in faster revenue or sales while lower ratio signifies lower sales or overstocking of inventory.
We then did an efficiency benchmark across major OEMS as visualized below:
The Framework
Before we look at the trends & paradigms on how the future will look like for the automotive sector, let us have a framework to view how the industry is changing & what are the factors driving those changes:
- What are the current trends in the industry & it's challenges?
- What trends or underlying currents are expected to change or disrupt the status quo?
- How are the companies looking at these trends & what are they doing about it?
- What do these disruptive trends mean for the customer?
Current Industry Trends & Challenges

Over the last couple of weeks, we have been analyzing the automotive industry from high level market summary to individual value chain players. A summary of key industry trends & challenges currently facing the industry are :
- Stagnating global production. Worldwide sales growth is slow (1.6 - 1.7% in 2024 - 25), reaching almost 89.6 - 91.6 million units. (Source : here). Growth is concentrated in China & Global South while stagnating in Europe & North America. (Source : here)
- Low EBIT Margins - Industry EBIT margins hover between 4.7 - 6.0%. Margins are expected to remain under pressure (Source : here)
- Policy Uncertainty - Tariffs, inflation & policy uncertainty compound issues around cost & profitability concerns. Rising local content rules for tax &/or tariff exemption.
- Regulatory Compliance - New Regulatory rules being added which adds to costs of compliance without immediate revenue benefits like: (Source : here & here)
- New Emission standards like Euro 7, US EPA GHG, ZEV mandates etc.
- Sustainability & ESG disclosures like EU CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) & CSDDD (Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive).
- Digital Product Passports in the EU
- Safety & Autonomous vehicles Regulations
- Consumer protection, privacy & data security
- Inflexible cost structure - The high fixed cost base (~ 91%) puts pressure on EBIT & provides limited margin opportunities through pricing changes due to competition & also limited flexibility to adjust during demand fluctuations.
- Price Competition - Related to the above, intense competition & related pricing pressure, particularly in China, are forcing manufacturers to absorb cost increases rather than pass them to consumers due to competition (Source : here)
- Regional Shifts - Asia, especially China has become an epicenter of vehicle production & sales, outpacing traditional production giants such as US, Japan & Europe. By 2023, China manufactured over 26.1 million vehicles - over 3 times Japan's output (Source : here). India's automotive industry is also on a growth trajectory, which along with Indonesia & other countries of the global south are poised to be key contributors to the industry in future (Source : here)
The automotive industry is currently in the maturity stage of it's life cycle which is characterized by
- Slower growth
- High competition
- Market saturation &
- Focus on efficiency & incremental innovation.
But, like a larva transforming into a beautiful butterfly, the industry is on the verge of a significant transformation driven by new trends & paradigms. What are those trends & paradigms?

Transformative Disruption
As we mentioned above, while the automobile industry is in maturity stage, it is not in decline. Like the butterfly above, it is evolving with new paradigms & trends. Let us now understand what are the new trends & paradigms disrupting & transforming the industry :
- Electrification & Energy Transition
- Software-Driven Vehicles
- Autonomous Driving & ADAS
- Mobility-As-A-Service (MAAS) & Shared Transportation
Let us understand them one by one :
Electrification & Energy Transition

The shift to electric vehicles (EVs) have been accelerating over the past couple of years. Automakers are rolling out affordable & more technologically advanced EV models driving the shift from IC (Internal combustion) vehicles to EVs.
Traditional IC (Internal Combustion) engine vehicles, which was the earlier paradigm, is now losing market share to EVs as consumers & governments push for greener transportation options & consumers have comparably advanced facilities in EV models compared to ICs.
EVs now represent ~20% of global car sales (up from < 2% in 2015), with China leading at > 30% market share. By 2030, ~ 50% of all vehicles marketed will be EVs. (Source : here)
However, EV sales are expected to slow down temporarily due to the following reasons :
- Ongoing trade tensions between China & the West
- Competition with Chinese EVs
- Infrastructure challenges (availability of charging stations, supply chain issues etc)
Due to the above, hybrid vehicle sales are gaining momentum as an intermediate option as they combine electric power with the reliability of combustion engines. Compared to EVs, they don't require charging but reduce carbon emissions. Hybrid vehicles provide the best of both worlds of lower emissions and enhanced fuel efficiency without the need for charging. In 2024, hybrids saw a YoY growth of almost 19%, which is expected to grow to over 23% by 2025. (Source : here)
Also, traditional IC engine vehicles face phase-out timelines (EU Ban by 2035) forcing the transition to EVs.
Software Driven Vehicles

The automotive industry is moving toward using software to design vehicles with new enhanced features and functionality, which will enable constant upgrades and new features over the vehicle's lifetime. This represents a significant shift from traditional vehicle development.
Many traditional OEMs are behind in this space compared to Chinese and tech-forward OEMs, who are already designing their vehicles using software. Closing the gap with Chinese and tech-forward OEMs presents a significant hurdle for traditional OEMs given their current business model.
This trend is gaining traction in 2025. For e.g., Honda is going to partner with Amazon Web Services to improve data collection and software updates and in such a way speed up the transition to SDVs. (Source : here)
Autonomous Driving & ADAS

Autonomous driving is one of the most prominent applications of AI in the industry. It incorporates various AI-powered technologies like adaptive cruise control, automatic emergency braking, and lane-keeping assistance, allowing vehicles to navigate complex road conditions autonomously without human intervention. These systems can detect objects, evaluate road environments, and make real-time decisions to further enhance safety and comfort.
While fully autonomous vehicles are still under active development, advancements in semi-autonomous driving systems are already making a significant impact. These advancements are redefining what it means to drive. With AI-powered systems providing real-time feedback & taking action autonomously based on the feedback, drivers can now experience greater convenience, such as hands-free highway driving, while maintaining a higher level of safety.
Global Autonomous vehicle market projected to grow from $ 60.3 billion (2025) to $ 449 billion (2035). (Source : here)
Mobility-as-a-service & Shared Transportation
The shift towards Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) is fundamentally changing the way people view transportation. As consumers increasingly prioritize access over ownership, traditional car ownership models are being challenged. Ride-sharing, car-sharing, and subscription services are rapidly expanding, especially in urban areas where convenience and cost-effectiveness are top priorities.
This shift is forcing automakers to rethink their revenue models. Instead of relying solely on vehicle sales, automakers are now exploring alternative sources of income through MaaS platforms. Companies like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Ford are investing heavily in services that allow consumers to pay for access to vehicles on-demand rather than buying a car outright. This transformation is opening new avenues for automakers to tap into ongoing service revenues, including subscription-based vehicle features and ride-hailing partnerships.
Now that we know the major trends or paradigms disrupting & transforming the automotive industry, how are the players in the industry looking at these trends? Before we get into the weeds, we need to understand two concepts by which companies view disruption :
- Profit Pools &
- Exploration vs Exploitation by Roger L Martin.