Strategy Byte - Week 59 The Crystal Ball - Part 2

Table of Contents
- Recap
- Profit Pools
- Profit Pool Shift
- References & Citations
Recap
During Week 58, we started analyzing the trends & paradigms changing the automotive sector to understand how the future will look like for the industry. To give a structure to our thinking, we developed a framework to
- View how the industry is changing &
- What are the factors driving those changes?
The framework we developed was as below :
- What are the current trends in the industry & it's challenges?
- What trends or underlying currents are expected to change or disrupt the status quo?
- How are these companies looking at these trends & what are they doing about it?
- What do these disruptive trends mean for the customer?
We tackled the first two last week.
Current Trends & Challenges
We summarized the key trends & challenges facing the industry as :
- Stagnating global production
- Low EBIT margins
- Policy uncertainty
- Regulatory compliance
- Inflexible cost structure
- Price competition
- Regional shifts
The automotive industry is currently in the maturity stage of it's life cycle characterized by :
- Slower growth
- High competition
- Market saturation
- Focus on efficiency & incremental innovation
But, the industry is also on the verge of a significant transformation driven by new trends & paradigms.

Transformative Disruption
Below are the trends & paradigms disrupting & transforming the industry:
- Electrification & Energy Transition
- Software driven Vehicles
- Autonomous Driving & ADAS
- Mobility-As-A-Service & Shared Transportation
This week, we tackle the third point.

Disruption has been a constant factor throughout history. From Ford introducing the assembly line for automobiles which disrupted the horse carriage industry to automation in the 1970s & the internet in the 1990s, disruption has changed not only our way of life, but our perceptions & social conditioning.
Before we get into how companies react in disruptive situations, let us understand two key lens through which a company looks at when facing disruption -
- Profit Pools
- Exploration vs exploitation by Roger L Martin
Profit Pools
In Week 19 of Finance Bytes, we discussed Business Model Canvas. It is a strategic management & visualization tool that helps organizations design, describe & analyze their business models in a single page.
It is visualized as below:
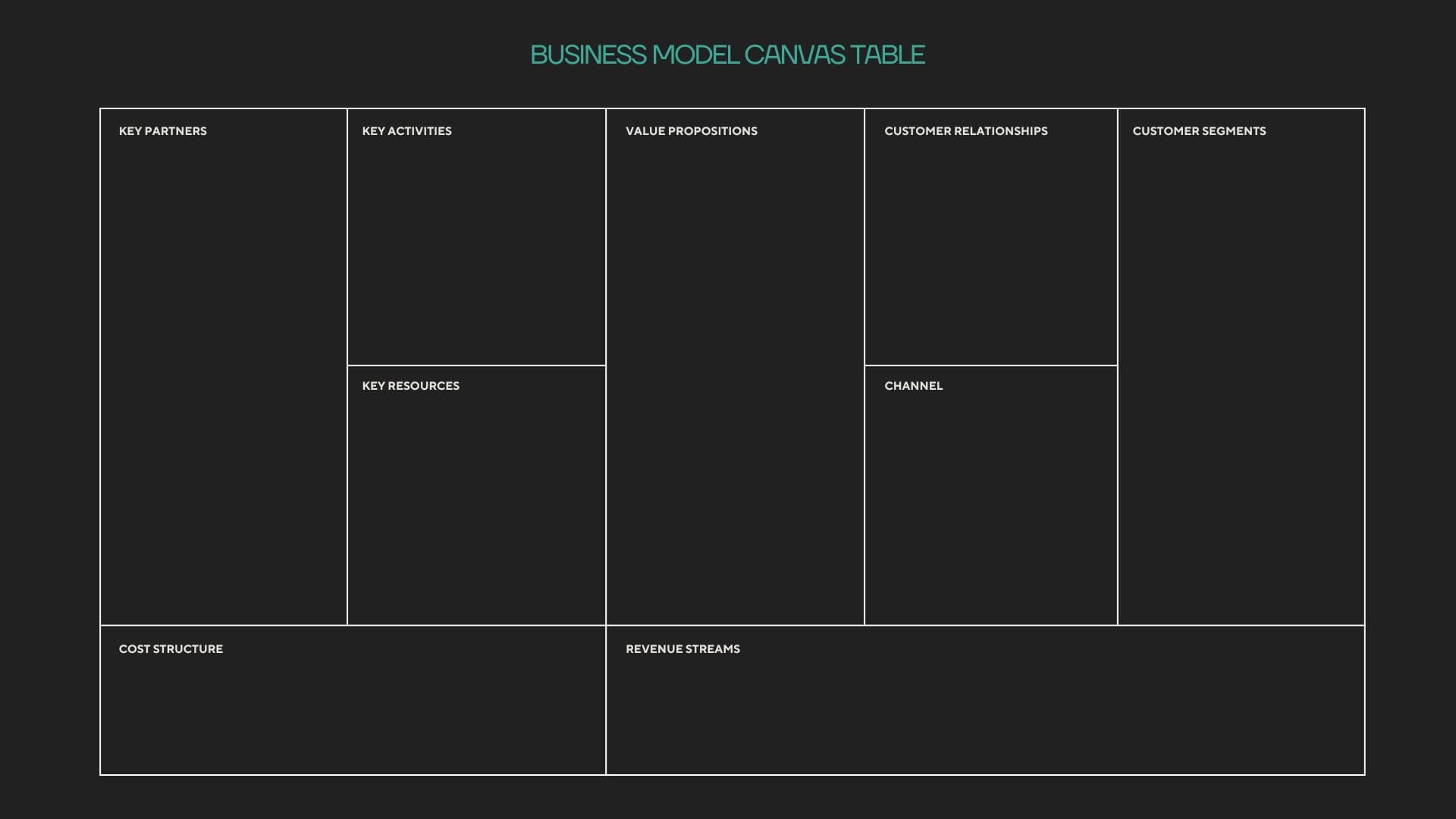
What do you understand from the above?
- A company engages in certain activities in line with their value proposition (also explained in Week 19 of Finance Bytes)
- It serves a selected segment of customers
- It acquires resources & converts those resources into outputs to serve those selected segment of customers
- It incurs costs to acquire & convert those resources to outputs &
- It develops certain processes & activities to serve those customers in the most efficient way possible to carry on it's business profitably
From the above, we can see that it is not only the internal activities of the company which result in profits, but also the interaction of the company with it's partners & customers, meaning it depends on how the value chain is structured. For e.g.,
Let us take the automotive industry value chain discussed in Week 51 :
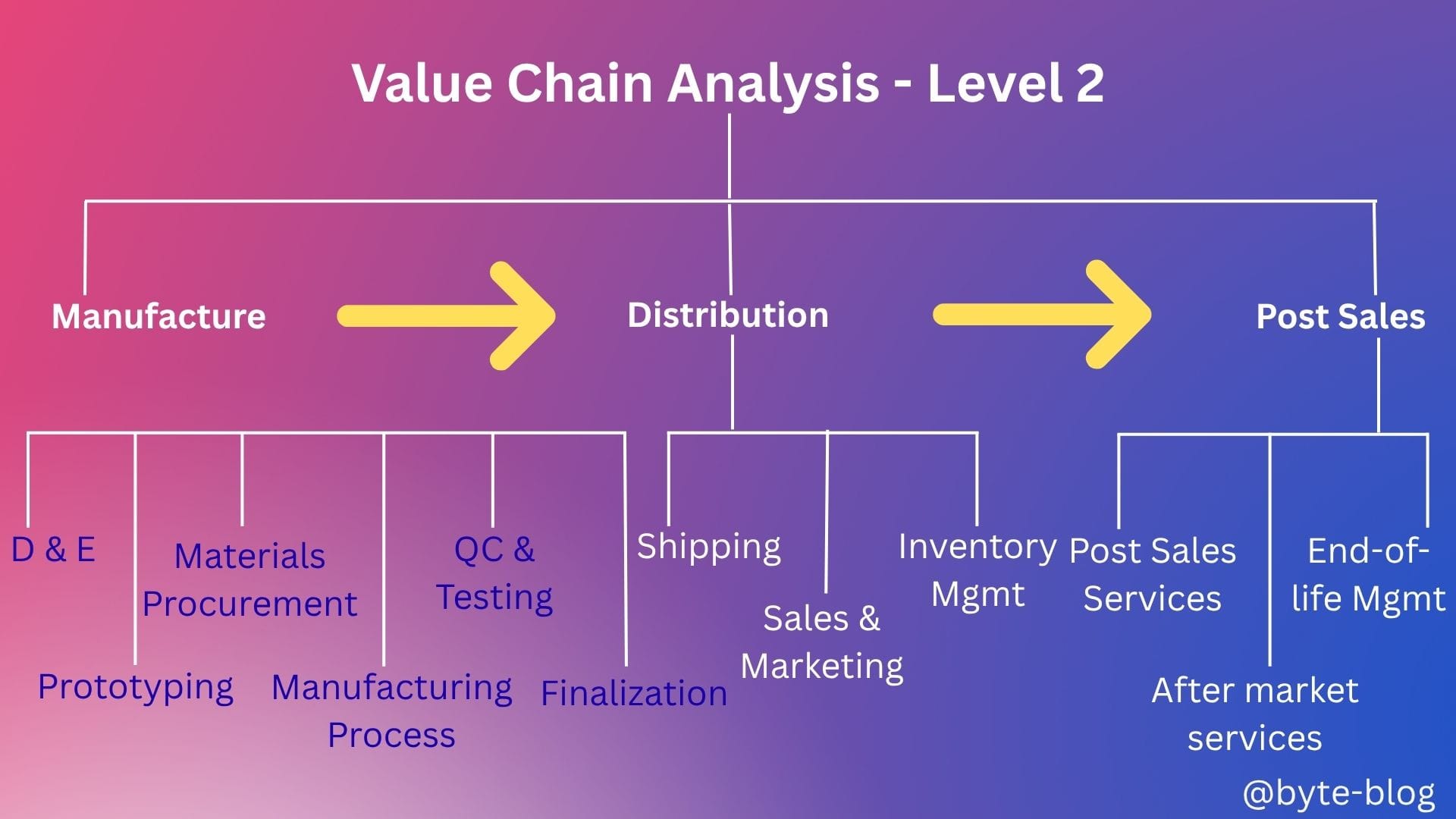
The traditional automobile industry business model is as below :
- Automobile suppliers provide parts to OEMs to manufacture & assemble automobiles
- The OEMs manufacture cars powered by ICE (Internal Combustion Engines)
- Distribution & Post sales activities include financing, servicing of vehicles etc.
A company along the value chain carries on activities related to that part of the value chain & generates profits. For e.g., a supplier generates profits selling parts to the OEMs, OEMs make profits in selling vehicles &/or post sales activities like financing or servicing etc. But which activity contributes more to the company's profit?
The part of the value chain or activity which contributes to the bottomline or profits for that company is called a Profit Pool for that section of the value chain. Let us now define it :
A profit pool is defined as the total profits earned across all points of an industry's value chain
The concept was developed by by Orit Gadiesh and James L. Gilbert which focused more on profits & not only on revenues.
The Profit pool concept tries to answer the most basic question about an industry - Where & how is the money being made?
Let us take the example of the US auto industry's profit pool : (Source : here)
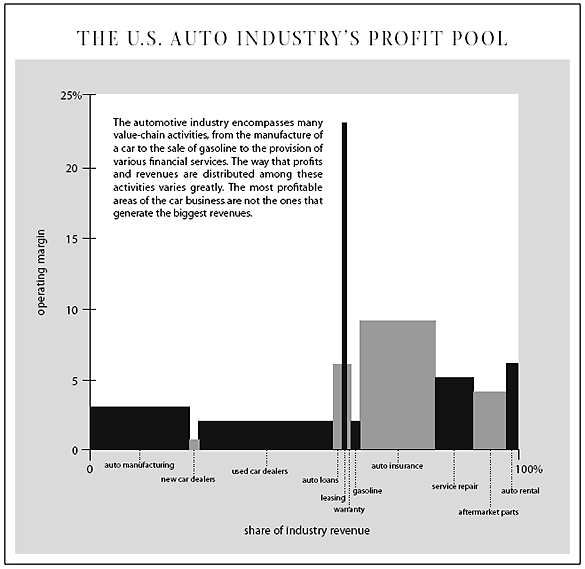
From the above, we can see that auto financing, insurance & after market servicing generates higher profits than manufacturing. The width of the individual bar charts denotes the amount of profits made while the height denotes the margin.
The questions which come to mind are -
- Why is manufacturing profit less than financing or servicing / repair?
- What are the trends driving auto leasing & insurance which generates higher margins compared to other activities in the value chain?
Understanding profit pools provides insights into sources of profits or which activities of the value chain contributes to the profits & the company can take action accordingly to increase it's profitability.
A very good example is Apple which shifted it's focus to software & app store where it's margins were higher compared to hardware. (Source : here)
Profit Pool Shift
Mapping & understanding profit pools over time shows how the industry evolved over that period of time.
- What were the sources of profitability previously or legacy profit pools?
- What changed in the industry - disruption or externally imposed changes like regulation?
- What are the new drivers of profitability or emerging profit pools?
In an industry undergoing transformation, the source of profits or profit pools will change. The activities which were a source of profit or margin today will dry up & new sources of profit or margin arises as a result of transformation.
Industry transformation or disruption can shift the profit pool or distribution of profits along the value chain.
Current Profit Pools
Traditionally, auto manufacturers & suppliers generate majority of their revenues & profits from some or all of the below activities:
- ICE Vehicle Sales / Service - Driven by new car sales, post-sales service
- Finance & Insurance - Auto loans, leasing & insurance
- Aftermarket Parts & Repairs - Repairs, parts & maintenance services
- Component Supplies - ICE components like battery, engine, car parts etc
However, as part of the shift from traditional ICE vehicles to EVs & software platforms, we can see specks of new profit pools such as:
- BEV / Vehicle Ecosystem - BEV sales, batteries, charging stations etc
- Mobility Services - Ride hailing, rentals, car-pools etc
- Automotive Software & Technologies - Software licensing & self driving systems
Traditional ICE vehicle business models dominate the profit pool, with service, finance & aftermarket service segments capturing most of the remaining share while BEV, mobility services & software are currently minor pools.
Emerging Profit Pools
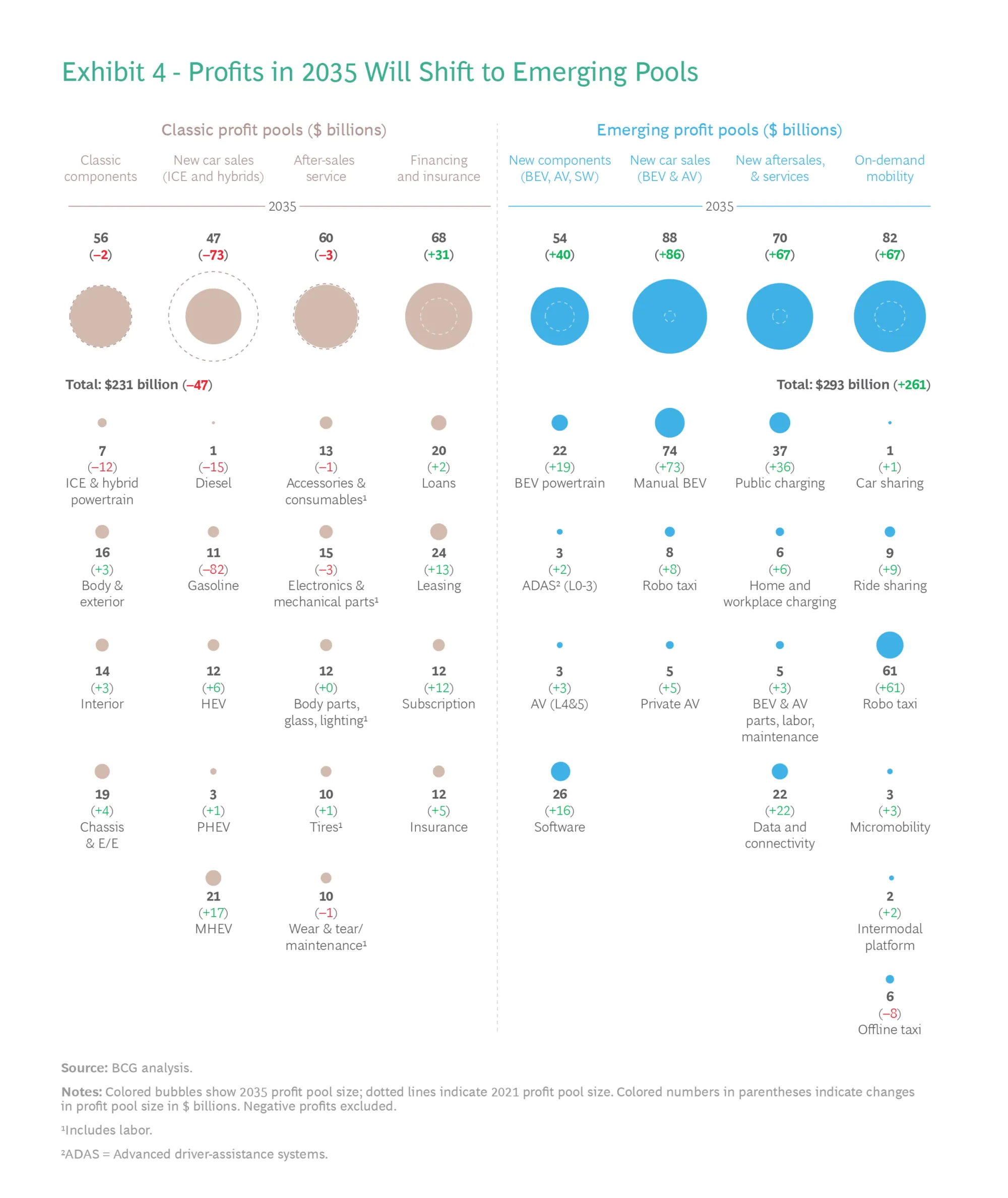
As per BCG analysis, emerging profit pools include
- Battery-electric & autonomous vehicles, the underlying component parts & software in those vehicles,
- Their servicing (including charging stations) &
- On-demand mobility (including ride-sharing apps, car-sharing services, robo taxis & micro-mobility options such as shared bikes & e-scooters)
It is expected that profitability from current profit pools in the automotive sector will decline through 2035. Profits from the sale of ICE (Internal Combustion Engines) including Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles (PHEV) will see the steepest drop, contracting by more than 60%.
Virtually, all revenue & profit growth in the industry will be concentrated in a small number of emerging segments - Battery-Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Autonomous Vehicles (AVs), software & components for EVs & AVs, & On-demand mobility.
The below visual from BCG shows the profit pool transition from current to emerging pools for the automotive sector:
Now that we know the lenses through which a company looks at disruption or transition, let us now see what they should be doing about it?
Would they disrupt their existing revenue & profit generating business to give way to a new & uncertain future? This leads us to another concept of Exploitation vs Exploration.